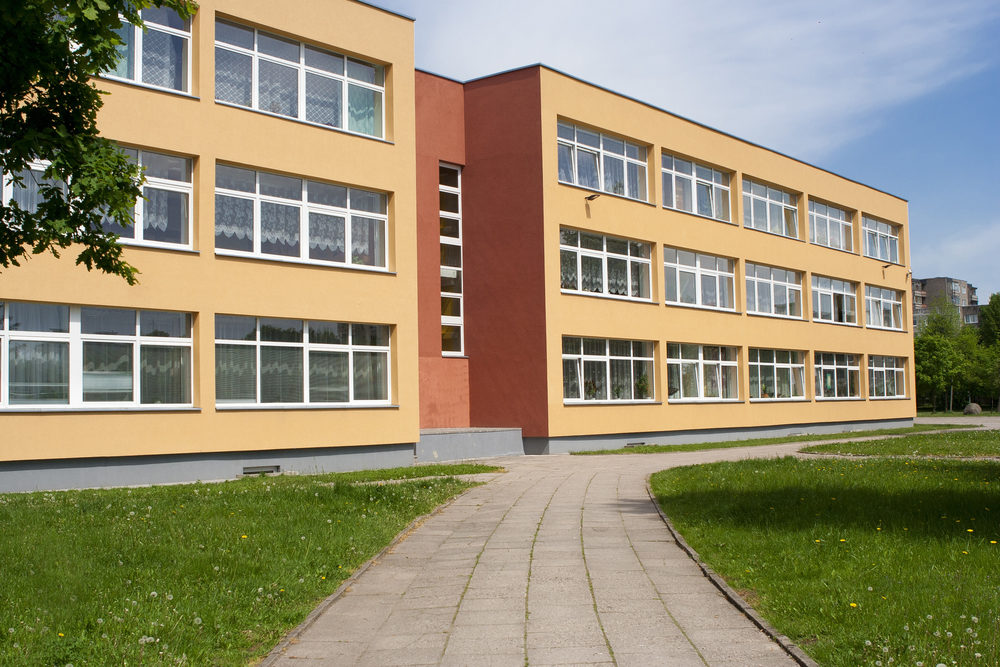
Loudoun County Public School Staff Member, William Smallwood, Suspended Without Pay After Soliciting Minor for Sex
Beware of Camp Lejeune Justice Act Fraud
Camp Lejeune Toxic Water Trials To Be Heard By Judge, Not a Jury
Recent Articles
Settlement Reached with Justice Department Following Massive CPAP Recall
Philips Respironics must stop producing sleep apnea devices in the U.S. until the manufacturer changes its safety measures per an agreement with the Department of Justice earlier this month. The government alleges that Philips violated the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FDCA) during its…
FDA Issues Alert Over Heart Pump Deaths
A device meant to improve the outcomes of heart patients in life-threatening conditions is under fire from the FDA for its risk of puncturing the heart. Abiomed, a medical device manufacturer owned by Johnson & Johnson MedTech since 2022, is recalling instructions for using its…
What To Look for When Hiring a Roundup Lawyer
Lawsuits filed against Roundup manufacturer Monsanto and now Bayer have been filed across the country and are in various stages before the court system. Some lawsuits have been settled while others are waiting for their day in court. Roundup lawsuits claim that there is a…
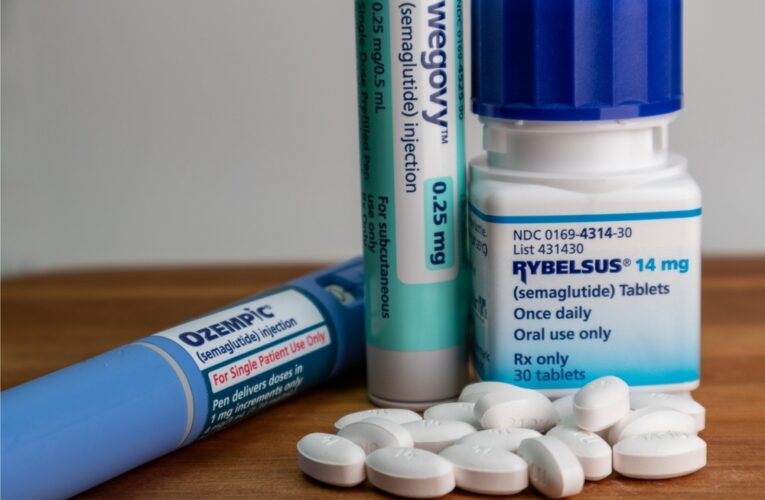
Diabetes Weight Loss Drugs Lawsuits Consolidated
The request to consolidate lawsuits against pharmaceutical companies Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly, who are under fire over the dangerous side effects linked to their explosively popular diabetes and weight loss drugs, was granted in February by the U.S. Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation (JPML).…
Camp Lejeune Claims Portal Now Available
Many military veterans who have filed Camp Lejeune claims are still waiting for resolutions nearly two years after the Camp Lejeune Justice Act became law. A long-anticipated online portal is now available for Camp Lejeune claims, which could help expedite the process and finally bring…
What Is the Most Common Cause of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
Certain medications designed to treat illnesses and symptoms in a sick patient can actually make things much worse by triggering a rare, intensely painful, and often life-threatening disease known as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS). SJS is a dermatological condition that begins with flu-like symptoms but quickly…
The FDA Gives Stamp of Approval to DNA Test Designed to Curb Opioid Abuse
With more than two million Americans battling opioid use disorder (OUD), the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved the first DNA test to assess whether or not a person is at an elevated risk of becoming addicted to the drugs. The AvertD test,…
Top 5 Reasons You Should Hire a Roundup Lawyer
For the millions of Americans who work in the agriculture industry or tend their yards, most are familiar with Roundup. This weed killer was introduced to the market in 1974 by Monsanto. In 2018, Monsanto was acquired by Bayer. Since its introduction, it has been…